Table of Contents
Toggle“A good education is the foundation of a better future”- Elizabeth Warren
From petrol to vegetable hikes, Inflation is raising the prices of everything. You might be so engrossed in the daily rising of prices, that you might not consider other sectors like education.
The education sector has seen a quantum leap in terms of inflation. This situation is worrisome for both parents and students as it impacts dreams & aspirations to enter a good college. Even the pandemic couldn’t stop education inflation from rising. How?
Well, for example, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) doubled its fee from 90,000 to 2 lakhs for an undergraduate course in 2023.
The majority of unprepared parents faced financial difficulties. Even those with a child education plan faced difficulties. However, if the case of inflation was considered while availing a child of education then those parents were off the hook!
How Will the Education Inflation Rate Impact in the Coming Years in India?
India’s consumer price inflation has indeed remained relatively stable, fluctuating between 5% and 5.6% over the past few years. However, education costs have outpaced this general inflation rate, with increases around 8% to 10%. This disparity in inflation rates has significant implications for families and individuals planning for education expenses. With education costs rising at 8-10% annually, the cost of education can potentially double every six to seven years.
Before getting into this, let’s first understand what education inflation is. As you can see from the image, it shows that the education inflation rate in India has surpassed both food and healthcare inflation rates.
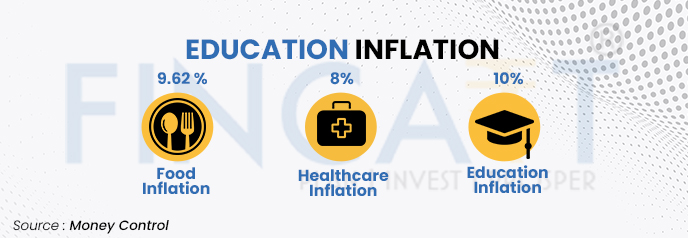
The reasons why education has taken a big leap are numerous. These factors come from a higher cost of living to increased tuition fees, from administration costs to technology & infrastructure, etc. Not only this, after all these costs come the hidden charges like exam registration fees, transportation costs, accommodation & food costs add further to it.
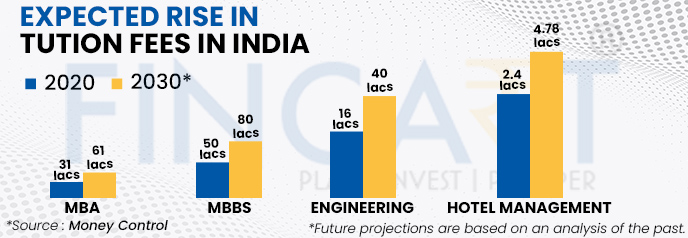
Increase in Tuition Fees
Over the years, an increase in tuition fees can be seen. There are comprehensive courses that have seen a hike in their costs. Not only this, mentioned below courses are expected to go up based on their hike in the previous years.
Having an education plan will help you to manage the coming inflation.
Expected Rise in Tuition Fees in India
Rise in Abroad Education
Rising inflation and the falling rupee value are damping the dreams of students who wish to study abroad. From education to living expenses, you can see a price rise. Due to this to manage the cost over there, many students take up part-time jobs as well.
When the cost of education is at its peak in India then imagine how much it will be abroad. Thus, for overseas education, a hefty amount is required. Did you know that the total cost of an undergraduate program at Harvard University for the academic year 2022-2023 has risen to 2.7% as compared to previous years?
According to The Hindu, “Last year, including visa, college fee, and other charges, a student would spend around 20 to 25 lakh per annum. This year, it will cost around 25 to 40 lakh per annum.”
Looking for a Financial Advisor?
Connect with Fincart for personalized financial advisory services and achieve your financial goals with confidence.
SIP: A savior in beating Education Inflation
A sudden deadline for paying the fees can become stressful. You might close your FD for that if you have any, take up an education loan, or could ask for financial assistance from your friends or family members.
But all the above stressful situations could be avoided if you just start saving for your child’s higher education. You can start by investing a small amount of money and increasing the amount per increment. The early and the longer you stay invested you get to experience the power of compounding.
Why SIPs for child education?
-
- For saving and investing, the most important thing is having financial discipline. This you can get with investing monthly in SIP because of its recurring nature.
-
- A fixed amount is set for every month’s SIP. Make sure to buy more when the price is low and buy less when the price is high. This benefits you from a lower cost of investing.
-
- The best thing about SIP is that you can start with Rs. 1000 per month and increase the amount as your increments or bonuses. Remember that little drops of water fill the mighty ocean!
-
- Early SIP investment can leverage you with the power of compounding and rupee cost averaging for an extended period.
Bottom Line:
Inflation is a silent killer that will kill you if not taken into consideration. When planning for financial goals like child education or even retirement, you must factor inflation into your planning.
Also Read: Things to Know About Child Education Planning
FAQs
What is education inflation, and how does it impact costs in India?
Education inflation refers to the annual rise in the cost of education, increasing expenses for tuition, fees, and materials, making it more challenging for families to afford quality education.
How has the cost of education changed in India over the years?
The cost of education in India has significantly increased, with tuition fees for schools and higher education institutions growing at a faster rate than general inflation, impacting affordability for many families.
How does education inflation affect middle-class families?
Education inflation puts a strain on middle-class families, forcing them to allocate more of their income toward educational expenses, often impacting their savings and other financial goals.
What is the average inflation rate for education in India?
The average inflation rate for education in India has generally ranged between 8-12% annually, outpacing general inflation and reflecting the growing costs in both school and higher education sectors.
How does education inflation impact higher education costs in India?
Higher education costs are heavily impacted by education inflation, especially in professional courses like engineering and medicine, making these fields increasingly expensive and sometimes necessitating educational loans.
How do private vs. public educational institutions contribute to education inflation?
Private institutions often charge higher fees due to infrastructure and facilities, contributing significantly to education inflation, while public institutions generally have lower fees but limited seats, intensifying competition and demand.




